My motivation for writing this post comes from recent
activity on Twitter about “coercive care” in psychiatry and an opinion posted
there by a psychiatrist suggesting that psychiatrists need to be aware of their
role as an agent of the state when they are engaged in involuntary treatment.
After seeing this I checked the literature and there were papers published on
the subject – so I thought I would write a post about the issue – specifically
whether coercion is an appropriate word to use and how it compares to
involuntary treatment as a description and a concept.
I don’t consider the issue lightly. For most of my career I have been in acute
care settings that required knowledge and skill in negotiating involuntary care
scenarios – specifically emergency holds, probate court holds, civil
commitments, conservatorships, and guardianships. That involved hundreds of
court appearances in 7 counties and 2 different states. I also testified as an expert on the issue of
prolonged state hospital stays for a patient advocacy organization and
testified in both malpractice cases and a criminal responsibility case. I have personally seen how local politics can
affect the civil commitment and conservatorship laws to the point that they are
actively ignored for various reasons. In that unstable landscape, the staff
responsible for treating the patient needs to be very flexible and innovative
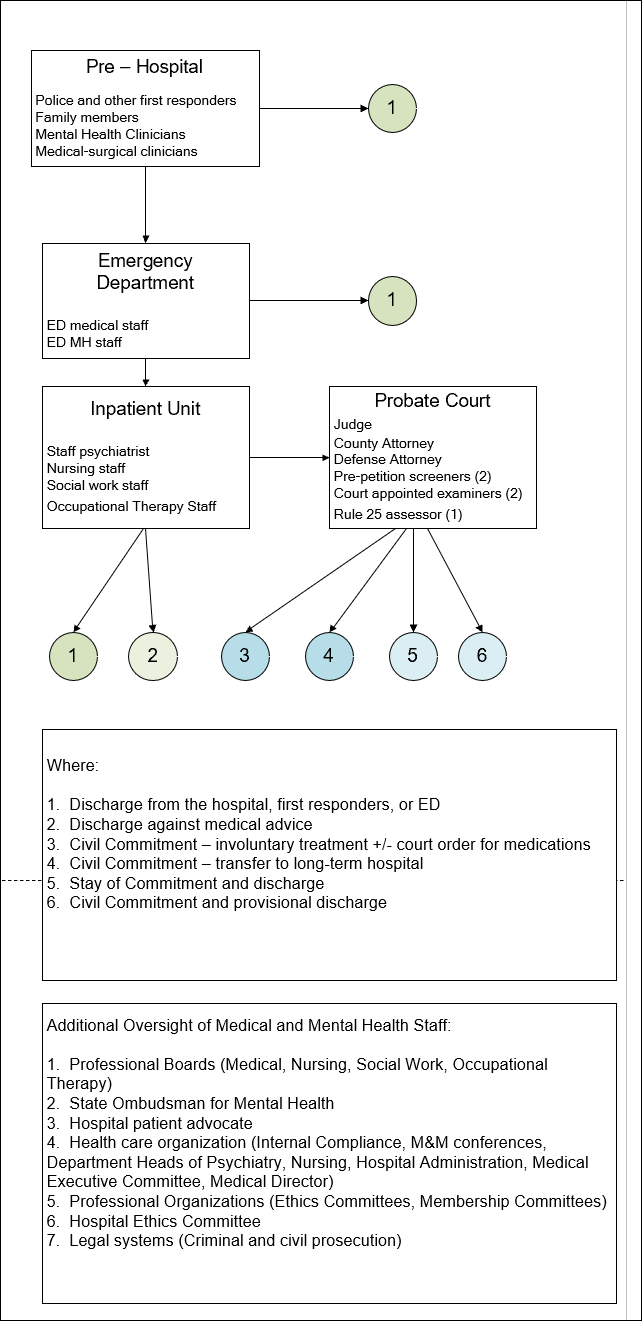
to provide the necessary care. The
following graphics show what that care generally looks like. It is a diagram of how involuntary treatment
gets initiated and carried out.
The commonest path is that there is an incident in the
community, emergency medical services are activated, and the patient is placed
on a hold and transported to the emergency department (ED). While there an ED physician and mental health
clinician (typically a social worker) makes and assessment of the patient and
determines if they can be discharged, admitted on a voluntary basis, or
admitted on an emergency hold.
Following the admission, the inpatient staff makes their
respective assessments and typically discuss their findings and the plan in
team meetings. If the patient was admitted on a timed hold (72 or 96 hours) and
a determination is made that the patient cannot be treated on a voluntary basis
prepetition screeners are contacted.
They come in and see the patient and collect more collateral information
than the inpatient team has access to.
They compile this in a prepetition screening document and in a team
meeting separate from the hospital staff (they are typically county employees)
make a determination that the hold will be cancelled or they will refer the
patient for further court intervention. If
they determine to not support the emergency hold, the patient is typically
discharged and it is illegal for a physician to immediately place them on
another emergency hold. If they are referred to the court a probable cause
hearing is held. At that point the judge
can release the patient or refer for a final hearing. Before any final hearing, 2 court appointed
examiners (typically a psychiatrists or psychologists employed by the county)
will see and assess the patient. They will testify in court and give specific
treatment recommendations to the court – independent of the hospital staff
charged with treating the patient. At the final hearing the patient can again
be released with no court intervention based on a judge’s decision. They can
also be court ordered to follow treatment recommendations including further
hospitalization and medications. Courts
can also accept a stay of commitment – meaning that the patient is not formally
ordered to accept treatment for a duration of time but they can accept
treatment and follow up and if everything is going well at 6 months any
involvement with the court self dismisses.
There is a similar intervention for persons who have been formally
committed called a provisional discharge. In that case, the person is
discharged with a plan to report back on outpatient progress. The structure of
this process highlights the fact that no single person or discipline makes a
decision about involuntary treatment. In addition, the statutory requirements
for mental illness or substance abuse do not specify any particular diagnosis
but depend on whether there is behavior that is self-endangering, harmful to
others, or significantly affects the person’s ability to function in their own
interest at the most basic level (adequate self-care in terms of food, housing,
and addressing significant medical problems).
The question critical to this post is how is this process
coercive rather than involuntary? And is there a difference between those terms? Just looking at standard definitions coercion
is clearly more insidious and it implies malignant intent. The Webster’s
definition is “to compel by force or intimidation; to bring about by force; to
dominate or control esp. by exploiting fear, anxiety, etc.” Using the same source, the definition of
involuntary is “not voluntary, independent of one’s will.” At this level, coercion is nothing medical
staff are ever trained to do and in fact would constitute a violation of
professional ethics. In psychiatry, the
training is focused on helping psychiatrists overcome standard biases that
people experience when interacting with others who have clear problems with
severe psychiatric disorders. The entire
focus of psychiatric training is developing a cooperative and helpful
relationship.
What about legal definitions and statutes pertaining to
coercion? The legal definition of
coercion is essentially the same as the dictionary definition: Verbal and/or physical threats and other
forms of intimidation in order to force someone to do something/not do
something that they are otherwise legally allowed/not allowed to do. Laws against coercion in federal statues
range from the obvious forms like sex trafficking to threats of retaliation for
political activity or exercising rights at work. In all of these cases, the
victims of coercion are generally going to be capable of making decisions in
their best interest but are unable to make willful decisions due to coercion.
It turns out that an entirely different level of analysis
has been applied to the issue of coercion and psychiatric patients. That level
of analysis is done by philosophers using thoughts about coercion from previous
works on ethics. For example, Schramme (2)
expands arguments from Frankfurt’s work to discuss specific examples of
coercion. He begins with the informed consent model. I consider Gutheil and Appelbaum to be
authoritative in this area and they discuss three elements of informed consent:
information, voluntariness, and competence (3).
The adequate information is discussed from the perspective of a
professional level of disclosure and also a “reasonable person” or the level of
information that most people would expect. The expected information varies from
state-to-state and in some cases for psychiatry there is a written information
standard. For example, in the State of Minnesota, antipsychotic medication
consent requires a signed consent form about those potential side effects. Voluntariness means consent is freely
given. It is often assumed that since psychiatric patients are generally
considered to be vulnerable adults who may be dependent on institutions that
this is a form of situational coercion. Gutheil and Appelbaum point out
that this would in effect not recognize the decisions made by large numbers of
people in institutions just because of the place they reside. They describe
more clearcut and explicit forms of coercion such as threatening the loss of
food or clothing if the patient does not follow recommended treatment. Competence
means that the patient has mental capacity to understand the information
presented and may a make a reasonable decision in order to give informed
consent. Psychiatric disorders can
affect all three elements of informed consent.
The philosophical look at coercion is a bit more complex
and it is selectively applied to the case of psychiatric care. Just looking at
the demographics raises some questions.
There are 1.3 million people in the US under guardianship or
conservatorship. At the same time there are 6.96 million people with dementia,
500,000 people with moderate to severe intellectual impairment, 36.25 million
with subjective cognitive impairment, and an undetermined number of people with
cognitive impairment and impaired capacity secondary to severe psychiatric
disorders. Those numbers suggest that there are not nearly enough guardianships
in place to provide substituted consent for people during medical
emergencies. In many jurisdictions
guardianships and conservatorships have to be pursued by family and that often
creates an undue financial burden. In the jurisdictions that actively ignore
conservatorships and guardianships – persons needing them often incur
unnecessary medical risk because treating physicians realize that they cannot
accept their consent to procedures involving risk – like surgeries.
Schramme has analyzed the issue of coercion in the following
ways. He breaks coercion down to threats and offers. For the purpose of his discussion, he states
that he is exclusively focused on autonomous choices that are contrary to
the will of the patient. These
choices cannot be made under the influence of threats but he outlines 3
scenarios where informed consent is lacking:
1. A patient is not
able to give informed consent – I think he makes a critical mistake here by
stating that most psychiatric patients are able to give consent and their
capacity is not globally impaired. It
clearly depends on illness severity and the stage of treatment. Most forensic
hospitals are charged with the task of restoring competency to mentally ill
offenders so that they can proceed to trial.
2. A patient
disagrees with treatment and makes that known but he is forced to accept
treatment anyway. The example given is a patient who if forced to take
medication because he is potentially dangerous to others. Schramme depicts this
as “a conflict between the patient’s will and the opinion of the doctor”. But where does the dangerousness come in? Why
is the patient unable to see that he is at risk from an extremely adverse
outcome (aggression and long-term incarceration or injury and possible death
due to a confrontation with the police) and not incorporate that into his
refusal?
3. A patient passively complies with a treatment
recommendation and does not make an overt decision. Schramme states that
although this would not typically be considered as coercive treatment – it all
depends on whether the consent is given freely or not. The implication is that
passive consent is not necessarily informed consent. Schramme invents the term “interactive
coercion” to suggest that psychiatric patients can be coerced by the
interpersonal relationship beyond what is typical of medical paternalism. That
presupposes that either nonpsychiatric physicians do not have relationships
with their patients, psychiatrists are masters at manipulating people, or some
combination.
From that point he goes on to provide 3 examples of interactive
coercion
Case 1: The psychiatrist
predicts that “damage or harm” will occur if the patient does not follow
certain course of action. This may or may not be coercion. Schramme gives the
example of taking away the patient’s cigarettes or writing them a suboptimal
report (the damage or harm) unless they comply with the prescribed course of
action. He acknowledges that harm can be
predicted due to non-compliance and it may not be a threat but a natural
consequence of untreated illness. Prediction of future causal events is a
warning and not a threat hence no coercion (p. 360). On the other hand, he suggests an “unusual” prediction
such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) if the patient had no previous
experience either it would constitute a threat.
The two necessary features for predicted harm to be a threat/coercion
would be that it needs to be intentional and unusual.
Case 2: The psychiatrist proposes a “detrimental unusual
consequence if the patient does not comply an example of effective threats as
coercion. In this case, if the threats are ineffective, they are
inconsequential, lead to no coerced decision. Schramme points out that “there
is no rigid line between a threat and a warning”. He gives an example of a
patient interpreting an action as a threat that may have had more to do with
the social roles of patients and nurses on the ward.
Case 3: The psychiatrist offers a beneficial unusual
consequence if the patient complies with a specific task. In this case there may
be intermediate conditionals. For example, the patient may not be motivated or
feel like socializing but forces themselves to do it anyway to get the offer.
Schramme introduces the idea of irresistible threats
and offers at this point. An offer becomes irresistible when there is no
other real alternative. In this case
even if the choice is voluntary, it can still be against one’s will. The best example is substance use disorders
where the person may not want to take the drug but acts on the drug as an
irresistible offer rather than a preferred motivation to remain abstinent. This
is an example of an offer that is irresistible and therefore coercive in that
it they are against the will of the person.
This is not a hard rule and Schramme emphasizes that all offers are not
bad and they depend on the subjective preferences of the patient. He goes on to develop the idea that “manipulation
and coercion – at least in psychiatric hospitals – do not only stem from predicted
consequences which bring people to do A, namely that they to prevent bad things
from happening.” (p. 367). Instead, he defines it as “an influence on the
autonomous will of the patient and not on the welfare of a person”. He closes by pointing out that institutional
and interpersonal dependencies can also result in irresistible offers to
psychiatric patients. He cites some examples
that today are irrelevant or exaggerated. For example – giving a patient
cigarettes if they take a medication or the offer of a “good report” for group
attendance. I have not observed either
of these happening on inpatient units over the course of my career even when
smoking was allowed on inpatient units. Even so, Schramme concludes that these coercive
offers are not necessarily morally wrong because “it might be good to
sacrifice the freedom of the patient for the sake of his well-being.” (p.
368). That is more than a trivial
distinction and I would argue is the basis of both civil commitment and
guardianship or conservatorship.
Szmukler and Appelbaum (4)
reviewed the coercion literature to date and described their own approach to
the issue of coercion. Their first step was noting that coercion was a loaded
term and describing a graduated systems of treatment pressures including:
(1) persuasion
(2) interpersonal leverage
(3) inducements
(4) threats
(5) compulsory treatment (in the community or as an
inpatient).
They provide an example of a community psychiatric nurse following
a patient in the community and how each of these pressures may work. They
develop models based on paternalism and capacity/best interests. Their definition of paternalism based on
previous research is given as:
“…a person is acting paternalistically towards another if
his action benefits the other; his action involves violating a moral rule with
regard to the other; his action does not have the other's past, present, or
immediately forthcoming consent, and the person believes he or she can make his
or her own decision on the matter. A paternalistic act requires justification
because it involves the violation of a moral rule but with the intention of
preventing a harm to the person.” (p. 240)
A series of questions is provided to answer whether or not
a paternalistic intervention is indicted. Answering those questions for a typical
emergency admission to an inpatient setting is typically balancing the deprivation
of personal liberty against death and disability. More subtle tradeoffs don’t end up as
admissions to inpatient units.
A capacity/best interest analysis is just the way it
sounds. The patient has impaired
decision making and is not able to make decisions in their best interest. Best
interest has a degree of subjectivity but the authors describe some general guidelines
based on previous work. The authors suggest that clinicians need a consistent
ethical framework for approaching these problems that is as rigorous as the
typical technical frameworks they use in practice.
“Protection of others” is described as a more difficult
problem for Szmukler and Appelbaum largely because of the subjectivity
involved. They discuss for example the low percentages of patients with mental
illness who are aggressive and the impossibility of prediction. They do not
mention that a number of features (acute care settings, acute threats, history
of violence/aggression, psychosis, pooling of cases, access to weapons) may greatly
increase risk but they are writing from the perspective of community rather
than inpatient care. They make an interesting comment: “Mental health professionals
may accept an obligation to notify appropriate authorities if there is a
serious risk of harm to others, but what is serious and who should instigate or
implement coercive responses is a matter for debate.” (p. 242). My understanding is that there is a
duty to warn in every state and the clinician not only needs to make a good
faith effort to contact the potential victim and take what other steps may be
necessary (eg. calling the police) to protect that person.
With that review, what assures that the term coercion is
not just another term used to inappropriately criticize monolithic
psychiatry? The standard dictionary
definitions implying malignant intent is certainly consistent with
inappropriate criticism. Schramme acknowledges
that there are situations where informed consent cannot occur due to a lack of
capacity but goes on to elaborate on treatment refusal where there is probably
lack of capacity and consent where the patient interactively coerced by
institutional or interpersonal scenarios. There is a high degree of subjectivity
involved in the interactive coercion scenarios.
Schramme seems to approach the problem hypothetically rather than
interactively. For example, as a clinical psychiatrist why would I ask if the
patient was perceiving a warning or a threat – I would just ask
them. In many cases agitated and paranoid patients are spontaneously accusing
staff of threats and malignant intent before any assessment or conversation has
occurred.
The best way I can think of how to proceed is to post a
vignette – in the standard way that they are posted these days – a composite of
features noted over the course of 25 years and not any specific patient:
Case Vignette
28-year-old man with schizophrenia and Diabetes
Mellitus Type 1 since age 8. He stopped treatment for schizophrenia a year ago.
Since then, he has been hospitalized for recurrent diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) four times and the
consult-liaison (C-L) team has noticed progressive cognitive problems. He is
discovered by the police in a park at night. The air temp is -5°F/-20°C
and he was not wearing adequate clothing (no jacket, caps or
gloves). In the ED he is noted to have a frostbite injury of his feet and
hands. He requests immediate discharge and states that he will follow up with
medical and surgical care on an outpatient basis. He refuses to consider
psychiatric care. He denies any hallucinations or delusions. He is admitted to the burn unit on a 72 hour
hold by the ED physician. Is this
coercion?
He is seen the next day by the C-L team. He has
some mild cognitive impairment and memory problems. He is detached and not saying much about why
he was hospitalized. His affect is restricted but he does not appear to be
depressed. He is requesting discharge but has no clear plan of what he will do
when he leaves. When asked about the
diabetes mellitus diagnosis he replies: “I can’t have it because I don’t have a
pancreas.” The C-L team recommends
referral to inpatient psychiatry and proceeding with a probate court
referral. The team speaks to a family
member there who talks at length about the family’s concern for the patient’s
safety and their relief that he is hospitalized. Is this coercion?
This is a realistic description of how patients are
admitted to acute care hospitals. The police officers in this case call EMS and
the patient is assessed by paramedics. The patient is taken to a local
emergency department where he is seen by a physician and a social worker and
admitted. In this case an involuntary hold is initiated by the police or by the
ED physician. A psychiatric diagnosis per se is not required since the
statutory definitions of mental illness are based on impaired judgement that
endanger the person or their health. Independently 6 people (none of whom were psychiatrists) agreed those conditions
existed.
He is seen and treated by surgery staff. He passively goes
along with treatment but there are obvious concerns about his capacity. Is this
a case of “interactive coercion” by surgical staff per Schramme’s formulation?
He is non-disclosing with psychiatry staff but the key observation is that he
no longer believes he has diabetes because he no longer has a pancreas. This is not a basis for adequate medical
decision making or self-care and that is further documented by his 4 episodes
of diabetic ketoacidosis, continued inability to manage this condition and the
question of cognitive impairment after episodes of coma. This patient is
referred for civil commitment and will be seen by pre-petition screeners
(typically one screener but a team of 4-5 people make the decision), a defense
attorney, 2 court appointed examiners, and a probate court judge. A total of about 9 people are involved in a
process to determine if the patient meets statutory requirements for civil
commitment and whether treatment should be court ordered.
Looking at the formulations of both Schramme and Szmukler
and Appelbaum is instructive. The
probate court proceeding that I describe is clearly a safeguarded capacity/best
interest scenario. The patient clearly lacks the capacity to make an informed
decision and consent on the basis that he no longer recognizes that he has
diabetes or that it needs to be treated despite life threatening consequences.
It is very clear that he would not get adequate treatment of diabetes or the
frostbite injuries if he was not hospitalized, observed, and actively treated.
By their formulation they would say that maximum treatment pressure is exerted
by compulsory treatment. In the final analysis, the ethical issue is that the
patient is being deprived of his right to continue to wander the streets without
adequate clothing or medical treatment for the compulsory treatment. Apart from a magical immediate restoration of
capacity is there a better short-term solution that is better designed to
protect his rights? I don’t see any.
An additional consideration is the issue of agency on
the part of the inpatient psychiatrist.
That psychiatrist has a fiduciary responsibility to the patient. That
involves discussing all relevant aspects of diagnosis and treatment with the
patient, including the concerns about his ability to care for himself. Is that
psychiatrist an agent of the state or as some philosophers like to put it –
the will of the state is being enacted though that psychiatrist? Definitely not
and here is why – the will of the state is transacted through the commitment
court and all of those personnel. The treating psychiatrist is unnecessary for the commitment proceeding and the court is focused on what their examiners conclude. Psychiatrists have no personal stake in whether somebody is detained in
a hospital by a court order. In fact, without a court order it is an unlawful
detention subject to both criminal and civil penalties. Over the years I have had to discharge many
people because the court did not produce a timely court order or decided to release
the patient. Further, in the actual
hearing the opinions of the court examiners are the ones the judges depend on.
The only interest of the inpatient psychiatrist is making an accurate assessment,
making sure all of the patient’s medical problems are treated, and making the
optimal recommendations for medical and psychiatric care. The inpatient
psychiatrist is also talking with the patient on a daily basis assessing
progress and attempting to establish a good working relationship with the
patient whether or not a court hold is in place or not. That working relationship
is possible when the patient recognizes that there is no adversarial relationship
with the inpatient psychiatrist. In fact, the treatment of patients on court
holds should be indistinguishable from voluntary patients.
By Schramme’s formulation that patient is not a competent
consenter. As noted about his passive cooperation with the burn surgeons,
endocrinology, and the inpatient psychiatrist might be construed as interactive
coercion. There is also a chance that it might not be according to these
definitions because the psychiatrist is discussing adverse outcome with the
patient but the discussion is based on what has happened many times already. Even with compromised cognitive capacity the
patient is able to acknowledge this and the fact that he does not want to end
up in a coma in the ICU gain. Another important aspect of these discussions is the
psychiatrist is very neutral and not reactive or blaming. They are a sincere
expression of concern given everything that is going on an what has happened to
the patient.
A final consideration here is that both philosophical and
legal approaches to involuntary treatment probably do not capture what is
really happening. For example the will or the autonomous will is the focus of
both the coercion and the involuntary treatment discussion. Reading though any paper on the will,
illustrates that it is a vague, changeable, and completely subjective concept. It is also not constant over time. When
philosophers like Schramme write about it – the are typically referring to an
individual and not a class of people. It makes more sense to talk about a
person’s conscious state rather than an isolated will. Conscious states are complex and
multidimensional (6). Even though they
cannot be accurately measured at this point – on a clinical basis it can easily
be observed that conscious states can change from being adept at self-care and
day to day living to states where inadequate self-care becomes self-endangering.
It makes very little sense to think that the will or autonomous will
of a person experiencing a major psychiatric illness is constant over time. The
goal of treatment ideally is to restore the autonomous will and assist the
patient with getting back to their baseline.
I have had that confirmed many times by people who benefitted from that
process.
George Dawson, MD, DFAPA
References:
1: Bureau of Labor
Statistics. Occupational Employment and Wages, May 2020 29-1223 Psychiatrists https://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes291223.htm
2: Schramme T. Coercive threats and offers in psychiatry.
In. Schramme T, Thome J (eds). Philosophy and Psychiatry. Walter de Gruyter;
New York; 2004: 357-369.
3: Gutheil TG,
Appelbaum PS. Clinical Handbook of
Psychiatry and the Law, 3rd edition. Lippincott, Williams, and
Wilkins, New York; 2000; p. 153-162.
4: Szmukler G, Appelbaum
PS. Treatment pressures, leverage, coercion, and compulsion in mental
health care, Journal of Mental Health. 2000 17:3, 233-244, DOI: 10.1080/09638230802052203
5: Walter J.
Consciousness as a multidimensional phenomenon: implications for the assessment
of disorders of consciousness. Neurosci Conscious. 2021 Dec 30;2021(2):niab047.
doi: 10.1093/nc/niab047. PMID: 34992792; PMCID: PMC8716840.
Supplementary 1: Workforce exposed to involuntary treatment scenarios:
There are an estimate 30,451 working psychiatrists in the
United States. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics 25,540 are
employed and the rest are self-employed.
Since it is very likely that acute care psychiatrists are employed by
hospitals 4,160 are in General Medical and Surgical Hospitals and 3,550 are in
Psychiatric and Substance Use Hospitals. There are currently 37,400 members in
the American Psychiatric Association and that number may reflect
researchers and the retired. The total pool of psychiatrists
who might be involved at some level in involuntary treatment is about 7,710
from the acute care setting but that is likely a gross overestimate for
several reasons. First, not all acute care settings treat people on an
involuntary basis. In any metro area emergency medical services (EMS) generally
brings the patients to only those hospitals who can provide the full array of
emergency services. Second, even among psychiatrists employed in hospitals only
a small percentage of them will provide direct care to patients who are there
on an involuntary basis. Third, there are very few free-standing psychiatric
hospitals or substance use facilities that accept anyone on an involuntary
basis. It is very likely that less than 10% of the psychiatric workforce ever
provides treatment to people on an involuntary basis.
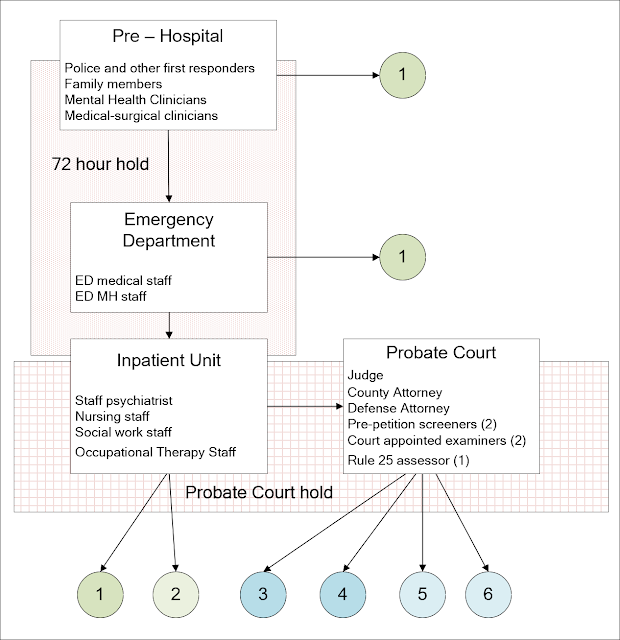
Supplementary 2: Graphic modification to show the emergency hold and probate court hold
Supplementary 3: Historical note
Although the patient is clearly safeguarded in the above process - some people might ask themselves: "Why don't we just abolish involuntary treatment and let things revert back to the way it was?" It would certainly make things a lot easier for psychiatrists. The short answer is that it is inhumane to people with severe mental illness and their families. The families are typically omitted from any discussion of involuntary treatment but historically they were charged with trying to contain a family member with severe problems. Patients in those situations often had catastrophic outcomes and even if they did not entire generations of family members were adversely affected by single family members with severe mental illness. That history is out there but it is difficult to find probably because of the stigma associated with those disclosures.