 |
| Dementia from Addictive Compounds |
As a geriatric psychiatrist and an addiction psychiatrist, what I see happening in both professional literature and lay literature is mind boggling. There is a clear bias advocating for the benign and even therapeutic effects of alcohol and addicting drugs. What most articles omit is that the health effects of alcohol are limited to no more than two standard drinks per day for men and one drink per day for women. The drinks cannot be all taken on the same day. The limits are per day not per week. Most of the evidence also suggests that the alcoholic beverage should be wine rather than beer or distilled spirits. Recent studies suggest that of the 70% of Americans who drink - about 1/3 of them are probably drinking in excess of those amounts. Doing the arithmetic that amounts to about 56 million people. Even a low percentage of brain injury will result in a significant number of cases od dementia. Moderate to heavy drinking (3-12+ drinks/day) carries the associated risks of high carbohydrate intake and sedentary life style. It is very common to find that moderate to heavy drinkers stop their usual outdoor activities and exercise and spend a lot of time watching television. This can lead to obesity, glucose intolerance and dyslipidemia and in the worst case scenario metabolic syndrome. All of those consequences lead to increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease.
There are addiction risks with alcohol consumption apart from atherosclerotic heart disease. Alcohol is proarrhythmic and doubles the risk for arrhythmia. In one large Danish study (11) they noted that alcohol intake and a history of atrial fibrillation was a risk factor for ventricular fibrillation. Some authors view alcohol use a risk factor in preventable atrial fibrillation. In clinical practice it is very common to interview patients with atrial fibrillation who notice that during times of heavy alcohol use they can sense that they are in atrial fibrillation and they spontaneously convert to sinus rhythm as their blood alcohol levels drop. Atrial fibrillation is a causative mechanism for embolic stroke and associated cognitive disorders.
The direct toxic effect of alcohol on the brain has been debated for years. Amnesia from Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is a known diagnostic entity related to thiamine deficiency associated with excessive alcohol use. It is probably underdiagnosed in most populations compared with postmortem diagnoses of the specific lesions consistent with Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (WKS). A large number of people with alcohol use problems have demonstrable cognitive effects on testing as well as structural and functional brain imaging brain imaging studies suggest some effect on brain structure. The lack of a pathological lesion has led some to suggest that this is a non-specific effect, but it is very likely that there are several variants of cognitive dysfunction related to alcohol use that are not associated with WKS (12). On a clinical basis it is very common to see patients with subjective cognitive impairment that typically involves working memory, declarative memory, and executive function. In treatment setting where abstinence from alcohol is assured many of these problems seem to clear up after about 60 days of abstinence. But there are also populations of people with varying degrees of anterograde and retrograde amnesia that is not as dense as expected with full WKS. Many of these patients are seen in treatment settings and never referred for comprehensive assessments of their cognitive disorder. To my knowledge there have been no studies looking at the issue of whether or not partial amnestic states correlate with WKS lesions at autopsy.
The problems with recognizing and treating cognitive disorders associated with substance use problems are exemplified in the first few paragraphs about alcohol. They are no less important for other commonly abused substances. In the case of stimulants, amphetamine analogues are known neurotoxins. Studies by Volkow and others have shown persistent changes in dopaminergic neurons up to 15 months after the last use. This may correlate with a persistent attentional deficit that leads patients to conclude that they now have attention deficit disorder. Additional brain insults from hemorrhagic strokes and cardiovascular problems associated with long term stimulant use are common. Stimulants are well known precipitants of acute myocardial ischemia and brain complications from hypoperfusion and emboli. Acute hypertension and tachycardia are part of the acute intoxication syndrome that can lead to hypertension and hemorrhagic stroke. This recurrent cycle leads to commonly observed complications of cardiomyopathy in the 4th and 5th decades of life and heightened risk of ventricular arrhythmias and cardiac arrest.
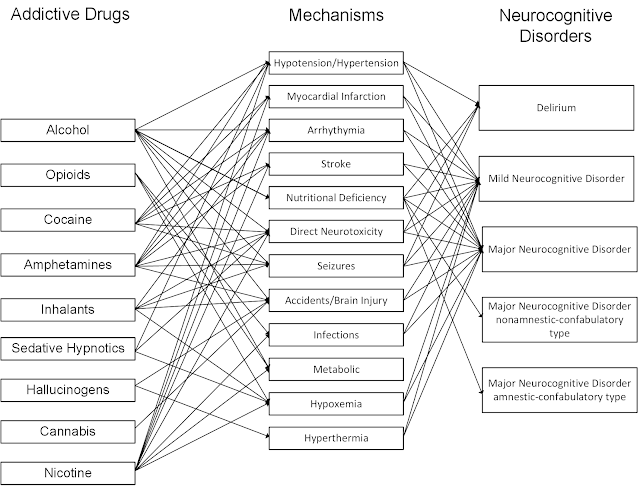
The graphic at that top of this post is not exhaustive - but point out some significant acute and chronic complications of drug use that can lead to permanent brain injury. These mechanisms cannot be overlooked as avoidable causes of dementia. I will be trying to elaborate on this graphic in the future to look at developing a review in this area. Any acute acre and addiction psychiatrist is probably more aware of these syndromes and complications because they are encountered in clinical practice. I have not seen any formal estimates of the fraction of dementia cases are preventable by avoiding these compounds. The largest fraction of dementia cases would likely be attributable to the most commonly used drugs - tobacco and alcohol. Drugs that kill more people acutely on a proportional basis like stimulants and opioids probably leave fewer survivors with dementia as a complication.
Contrary to the conventional wisdom these days - avoiding dementia is another strong argument for a sober life style.
George Dawson, MD, DFAPA
References:
1: de Gaetano G, Costanzo S, Di Castelnuovo A, Badimon L, Bejko D, Alkerwi A,Chiva-Blanch G, Estruch R, La Vecchia C, Panico S, Pounis G, Sofi F, Stranges S, Trevisan M, Ursini F, Cerletti C, Donati MB, Iacoviello L. Effects of moderate beer consumption on health and disease: A consensus document. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 Jun;26(6):443-67. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2016.03.007. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Review. PubMed PMID: 27118108.
Moderate consumption is defined as 1 drink per day in women and 2 drinks per day for men in a non-binge drinking pattern. J-shaped dose-response curve
2: Fernández-Solà J. Cardiovascular risks and benefits of moderate and heavy alcohol consumption. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Oct;12(10):576-87. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.91. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Review. PubMed PMID: 26099843.
U-Shaped dose-response curve
6: Bathla M, Singh M, Anjum S, Kulhara P, Jangli S IIIrd. Metabolic syndrome indrug naïve patients with substance use disorder. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2016 Sep 3. pii: S1871-4021(16)30183-7. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2016.08.022. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 27618517
Alcohol was the main substance used by patients meeting WHO criteria for Metabolic Syndrome.
7: Vancampfort D, Hallgren M, Mugisha J, De Hert M, Probst M, Monsieur D, Stubbs B. The Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Alcohol Use Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Alcohol Alcohol. 2016 Sep;51(5):515-21. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agw040. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Review. PubMed PMID: 27337988.
1 person in 5 with alcohol use disorder has metabolic syndrome.
Positive correlation between heavy drinking and metabolic syndrome.
9: Yousefzadeh G, Shokoohi M, Najafipour H, Eslami M, Salehi F. Association between opium use and metabolic syndrome among an urban population in Southern Iran: Results of the Kerman Coronary Artery Disease Risk Factor Study (KERCADRS). ARYA Atheroscler. 2015 Jan;11(1):14-20. PubMed PMID: 26089926; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4460348.
9: Yousefzadeh G, Shokoohi M, Najafipour H, Eslami M, Salehi F. Association between opium use and metabolic syndrome among an urban population in Southern Iran: Results of the Kerman Coronary Artery Disease Risk Factor Study (KERCADRS). ARYA Atheroscler. 2015 Jan;11(1):14-20. PubMed PMID: 26089926; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4460348.
Current opioid users had the highest prevalence of metabolic syndrome (39.6%) but the study was confounded by a high baseline rate in the controls (37.2%).
10: Brunner S, Herbel R, Drobesch C, Peters A, Massberg S, Kääb S, Sinner MF.Alcohol consumption, sinus tachycardia, and cardiac arrhythmias at the Munich Octoberfest: results from the Munich Beer Related Electrocardiogram Workup Study (MunichBREW). Eur Heart J. 2017 Apr 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx156. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 28449090.
11: Jabbari R. Ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death during myocardialinfarction. Dan Med J. 2016 May;63(5). pii: B5246. Review. PubMed PMID: 2712702.
12: Ridley NJ, Draper B, Withall A. Alcohol-related dementia: an update of the evidence. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013 Jan 25;5(1):3. doi: 10.1186/alzrt157. eCollection 2013. Review. PubMed PMID: 23347747.
Supplementary:
The calculation for the following observation:
Recent studies suggest that of the 70% of Americans who drink - about 1/3 of them are probably drinking in excess of those amounts. Doing the arithmetic that amounts to about 56 million people.
321M(current US population) - 80M (population less than drinking age) x 0.7 (percentage of population that drinks) x 0.3 percentage of excess drinkers = 56 million people.
10: Brunner S, Herbel R, Drobesch C, Peters A, Massberg S, Kääb S, Sinner MF.Alcohol consumption, sinus tachycardia, and cardiac arrhythmias at the Munich Octoberfest: results from the Munich Beer Related Electrocardiogram Workup Study (MunichBREW). Eur Heart J. 2017 Apr 25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx156. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 28449090.
11: Jabbari R. Ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death during myocardialinfarction. Dan Med J. 2016 May;63(5). pii: B5246. Review. PubMed PMID: 2712702.
12: Ridley NJ, Draper B, Withall A. Alcohol-related dementia: an update of the evidence. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013 Jan 25;5(1):3. doi: 10.1186/alzrt157. eCollection 2013. Review. PubMed PMID: 23347747.
Supplementary:
The calculation for the following observation:
Recent studies suggest that of the 70% of Americans who drink - about 1/3 of them are probably drinking in excess of those amounts. Doing the arithmetic that amounts to about 56 million people.
321M(current US population) - 80M (population less than drinking age) x 0.7 (percentage of population that drinks) x 0.3 percentage of excess drinkers = 56 million people.
